Plan Cache
Introduction
TiDB supports PlanCache for prepare and execute statements. By using PlanCache, TiDB can skip the optimization phase to gain some performance benefits.
There are several limitations to current PlanCache:
- Only support
prepareandexecutestatements, not support general queries; - Only session-level
PlanCacheis supported, cached plans cannot be reused across sessions; - Some complex plans cannot be cached, and you can see this document for more details;
Handling Prepare/Execute Statement
The process of handling a prepare statement is below:
- Parse the original SQL to an AST;
- Encapsulate the AST with some other necessary information(like
current-db,statement-text, ...) toCachedPrepareStmt; - Store the
CachedPrepareStmtinto this session'sPreparedStmtMap;
The process of handling an execute statement is below:
- Parse all parameters and store their values into this session's
PreparedParamMap; - Get the corresponding
CachedPrepareStmtfrom this session'sPreparedStmtMap; - Construct the plan-cache key with information in
CachedPrepareStmt; - Fetch a plan from the session's
PlanCacheby using this key, and:- if it succeeds, then
- check whether this plan is valid for current parameters, if it is, then
- rebuild the plan, and
- run the rebuilt plan;
- else, then
- optimize the AST in
CachedPrepareStmtwith current parameters to get a new plan, - store the new plan into current session's
PlanCache, and - run the new plan.
- optimize the AST in
- if it succeeds, then
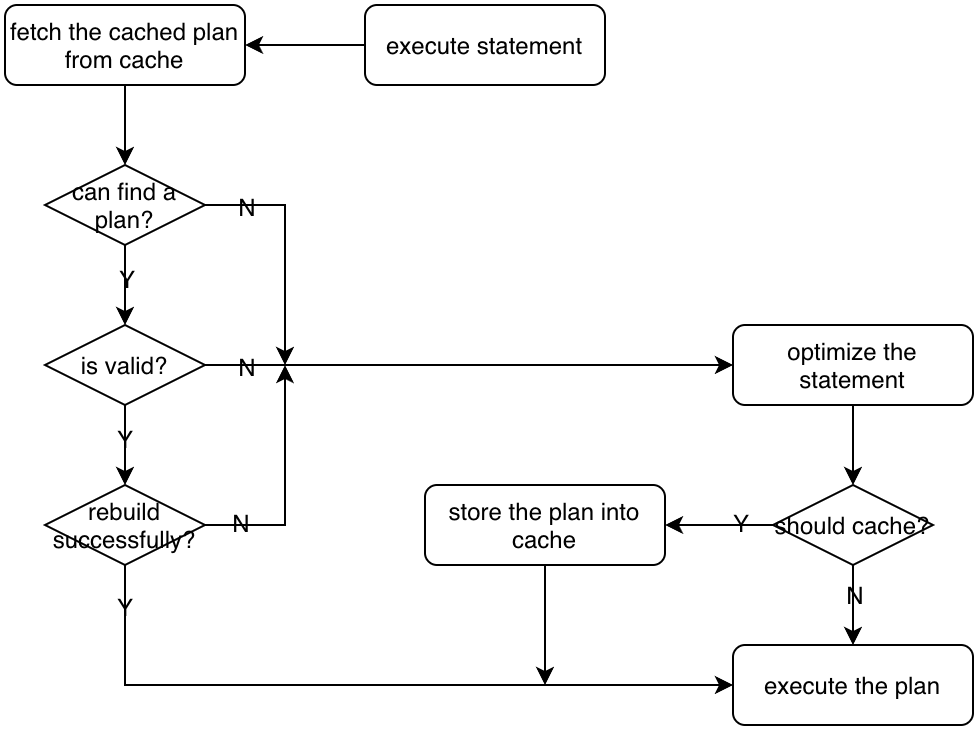
The main function of handling execute is common_plans.go:Execute.getPhysicalPlan().
Plan Rebuilding
A cached plan cannot be reused directly unless it is rebuilt. The main goal of rebuilding is to re-calculate the access range.
For example, if the query is select * from t where a<?, when you first execute it with 1, then a TableScan with range (-INF, 1) could be generated and cached, and then you later execute it with 2, the range has to be re-calculated to (-INF, 2) so that it can read correct data this time, and that is what plan rebuilding does.

The entry function of plan rebuilding is common_plans.go:Execute.RebuildPlan().
The Parameter Maker
Parameter Makers are used to propagate current parameter values to executors(operators).
For example, if the query is select * from t where a+?>1, then the filter a+?>1 will be converted to a Selection operator with an expression-tree a+?>1:
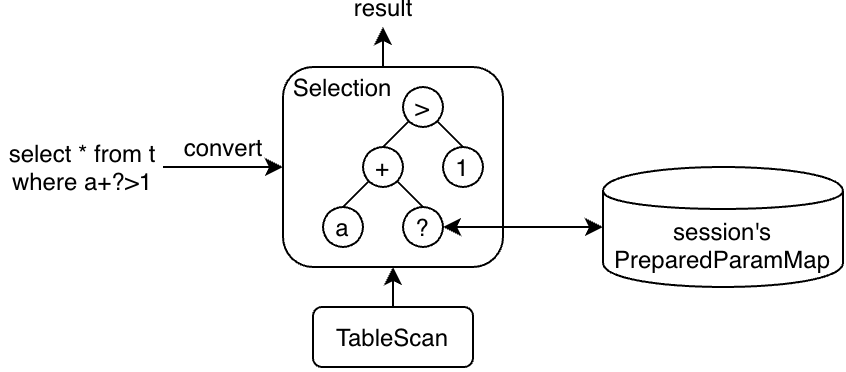
The parameter placeholder(?) is converted to a ParamMaker in Constant.
You can regard it as a special kind of pointer, and when the plan is processed and the parameter's value is needed, we can use it to get the corresponding value of this parameter.
type Constant struct {
...
ParamMaker *ParamMaker
}
func (c *Constant) Eval(row) Datum {
if c.ParamMaker != nil {return c.ParamMaker.GetUserVal()}
...
}
func (d *ParamMaker) GetUserVal() Datum {
return d.ctx.GetSessionVars().PreparedParams[d.order]
}